This post highlights What is SEO and How does Optimize A Webpage For SEO
When we search in a search engine like Google, we basically search the index of Google. This is true for any content management site and social media site. The words or phrases we type (known as Keywords or Key-phrases) are the basis on which a search engine displays the result (SERP). A search engine optimized page thus should be the one that ranks in the top few ranked pages. To achieve that, we must first understand as to what a Search engine does to find results based on the query (typed words).
Ranking of a Webpage by Search Engine?
Web Crawling
What is published out on the World Wide Web if found by search engines using automated programs. This action of searching the World Wide Web by the program also called crawling. The programs which do this work are called bots /crawlers /spiders / web crawlers. Essentially, crawling is copying what is on web pages and repeatedly checking the multitude of pages to see if they are changed and make a copy of any changes found.
(Ref https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_bot)
Indexing
Next comes storing of this copied data by crawlers in search engine data centers. The repository of web pages is referred to as the ‘Index’. Indexing is the process of organizing the masses of data and pages so they can be searched quickly for relevant results to your search query.
Search Algorithm
Next comes returning these stored web pages in order of relevance when a search is made. This requires ranking of web pages to ensure that one gets the most relevant pages first in the result of a search. The search engines use inbuilt algorithms to rank pages.
But How Much Does A Search Engine – Actually Search?
- As of 2020 there are over 1.74 billion websites on the Internet
- Google processes over 7 billion search queries every day worldwide
- 15% of queries are absolutely new
- There are over 600 million blogs in the world in 2020
- More than 5,760,000 blog posts are published on the Internet every single day
- 6.7 million people regularly publish blog posts.
(Ref – https://www.websitehostingrating.com/internet-statistics-facts/)
So How does a Search Engine Rank Pages then
It does it by evaluating the pages against certain inbuilt queries, in fact over 200 of them! These queries are built into the algorithm. Typical queries are – Does this page contain your keywords? Are the keywords in title or URL? Is the page from a quality website? What is this page’s page-rank? How many outside links does the page have and how important are they? And many more…
Answers to all the questions give a page its overall score and the search engine returns our search with a result according to the overall scores. The fact that 75% of people never scroll past the first page in search results makes it important for business owners / digital marketeers / content writers to make sure that their page has a good overall ranking.
And Finally – How Do We Optimize Our Page – SEO?
Keywords & Key-phrases
The words and phrases that searchers enter any search engines, are called “keywords” or “key-phrases”, also called “search queries”. A search engine matches the search with the key words with which it has indexed the pages. To ensure that more search traffic is directed by the search engine to a website, it is imperative that the keywords on the page are relevant to what people are searching for so they have a better chance of finding the content among the results.
Keywords can be broad and far-reaching (these are usually called “head keywords”), or they can be a more specific combination of several terms — these are often called “long-tail keywords.” Long-tail keywords usually have more clearly defined intent. Also the long-tail keywords have less competition, with room for a smaller site to break in and make their mark on the SERPs.
It yields the best result if the URL, a heading or H1 tag on the page, the meta description, and alt attributes of images on the page contain the keywords. This will emphasize the content of the page to the search engines.
A focus keywords / key-phrase should be used only once. The main reason why one should not use the focus key-phrase more than once is to avoid competition within the pages for a position in Google. This phenomenon is called keyword cannibalization. If one optimizes two different articles for the same focus key-phrase, it is like telling Google that both are suitable for people searching for that keyword!
URL’s
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed a web address,is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. It is good idea to write URLs in a manner that contains relevant text to the post or page content. Also, including keyword terms in URLs is a good idea. Doing as such will helps one rank higher for keywords related to the content and it gives visitors another visual to let them know what kind of content they can expect from the page. Underscores should never be used in URLs.
Headings
Headings help users and search engines to read and understand text. For example, they act as signposts for the readers and make it easier for them to figure out what a post or page is about. Headings also help readers to understand the important parts your content and show how they are interconnected. Using headings creates texts of higher quality that are also easier to read. A better text is better for users, which is better for SEO. Search engines use headings to identify the most relevant parts of a posts, as well as indexing the general structure and content of a site or blog page. (Ref (https://yoast.com/how-to-use-headings-on-your-site/), https://ilizien.com/7-best- ways-of-writing-headings-of-posts-email/). Tips: –
- Include modifiers like “best”, “2016” etc. to stand out and to pick up long tail searches.
- Keep title tags 55 characters or less or they’ll appear truncated in search results (Ref https://www.udemy.com/course/learn-digital-marketing-course/).
Meta Description
The meta description is an HTML attribute that provides a summary of a web page. Search engines such as Google often display the meta description in search results, which can influence click-through rates.
However, while it is true that Meta Descriptions do not contribute to Search Engine Optimization – SEO directly, they do help in higher click through ratios by searchers.In addition to the title tag, meta description is an especially important factor to consider. The content of meta description provides an opportunity to “advertise” content to searchers, and searchers’ chance to decide whether the content is relevant and contains the information they’re seeking from their search query. Tips: –
- Highlight the benefit of your post or product compared to competitors who already appear in the search results.
- Keep meta descriptions 160 characters or less or they’ll appear truncated in search results.
Image alt Attributes
Adding images to articles encourages people to read them, and well-chosen images can also back up the content and yield a good ranking in image search results.The alt and title attributes of an image are commonly referred to as alt tag or alt text and title tag. But technically, they are not tags, they are attributes. The alt text describes what is on the image and the function of the image on the page. alt text strengthens the content of the articles with search engine spiders and improves the accessibility of website.
External Links
Search engine ranking factor survey data has shown that getting external links is the single most important objective for attaining high rankings (for SEO). This stems from the idea that external links are one of the hardest metrics to manipulate and thus, one of the best ways for search engines to determine the popularity of a given web page. External Links are hyperlinks that point at (target) any domain other than the domain the link exists on (source). In layman’s terms, if another website links to other, this is considered an external link to the website. Similarly, if one website links out to another website, this is also considered an external link. Today, the major search engines use many metrics to determine the value of external links. Some of these metrics include: –
- Trustworthiness of the linking domain.
- Popularity of the linking page.
- Relevancy of the content between the source page and the target page.
- Anchor text used in the link.
- Number of links to the same page on the source page.
- Number of root domains that link to the target page.
- Ownership relationship between the source and target domains.
Internal Links
Google follows links to discover content on websites and to rank this content in the search results. If a post or page gets a lot of links this is a signal to Google that it is an important or high-value article. This counts for internal as well as external links. Internal linking is something in control of a site owner. With the right internal links, the site owner can guide the page visitors and Google to the most important pages.
Text length
There are higher chances of a ranking in Google if the content / post is long; of 1000 words or more. When the text is longer, Google has more clues to determine what it is about. The longer is the text, the more likely is that the focus key-phrase appears. Also, if a page consists of few words, Google is more likely to think of it as thin content. Thin content is content that has little or no value to the user. Google considers doorway pages, low-quality affiliate pages, or simply pages with very little or no content as thin content pages. All search engines want to provide the best answers to the queries people have. Thin content is less likely to offer a complete answer and satisfy the needs of the public. Consequently, it will probably not rank very high. (Ref https://yoast.com/text-length)
Website Performance & Speed
Google – support.google.com › webmasters has indicated site speed (and as a result, page speed) is one of the signals used by its algorithm to rank pages – SEO. And research has shown that Google might be specifically measuring time to first byte as when it considers page speed. In addition, a slow page speed means that search engines can crawl fewer pages using their allocated crawl budget, and this could negatively affect your indexation.
Page speed is also important to user experience. Pages with a longer load time tend to have higher bounce rates and lower average time on page. Longer load times have also been shown to negatively affect conversions. A one second delay in page loading speed can cost you 7% of your ecommerce conversions. Analyze your site with Google Page Speed Insights. Aim to score 80+. (https://moz.com/learn/seo/page-speed)
Mobile-Friendly Test
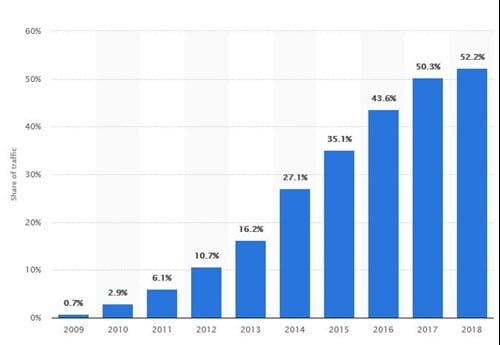
The internet searches on mobiles has overtaken desktop searches. See graph. It is extremely important as now Google’s algorithm favours mobile friendly sites. Pages that take a long time to load tend to have higher bounce rates. According to Google, 53% of mobile users leave a page if they are waiting 3 seconds for it to load, and if this number rises to 5 seconds, the chances of the visitor bouncing off increases by a massive 90%!
Conclusion – SEO
SEO is a continuous process. The ways to improve a page ranking is an ever-evolving process with Search Engines owners periodically modifying their algorithms for best customer experiences and SEOs around the world trying to improvise and understand the best they can of the algorithm. Internet is full of articles that list up to 200 of such measures to improve page ranking. While each of the steps can contribute to the page ranking, however, each of the measures will not yield equal results. The measures listed in this article are the measures that rank the highest in each of these articles and if t followed, will ensure a high page ranking.
Download the PDF of this article here!
Keep looking at this space for more updates. https://ilizien.com/blog/